



Hard drives have served us for many years, and they still find their place in most of our systems. With the reduction in costs, the number of users using only SSDs, shelving HDDs continues to increase day by day. Solid-state drives have changed a lot of things since they've been in our lives and have benefited us countless ways.
If you have purchased a new portable laptop over the last few years, you are probably using an SSD as the primary boot drive. On the other hand, if you have recently collected a desktop system, you must have received at least one SSD.
You may still be having trouble choosing between HDD or SSD. Let's briefly look at the differences between SSDs and HDDs. In particular, we will focus more on the benefits of SSDs.
SSD and HDD
Traditional hard drives are used as a basic permanent storage unit on a computer. So unlike data stored in RAM, data does not fly away when you turn off the system. HDDs, as you know, have a magnetic coated metal plate that stores your data. The read/write head is used to access data when the plates rotate. So we're talking about a completely mechanical system.
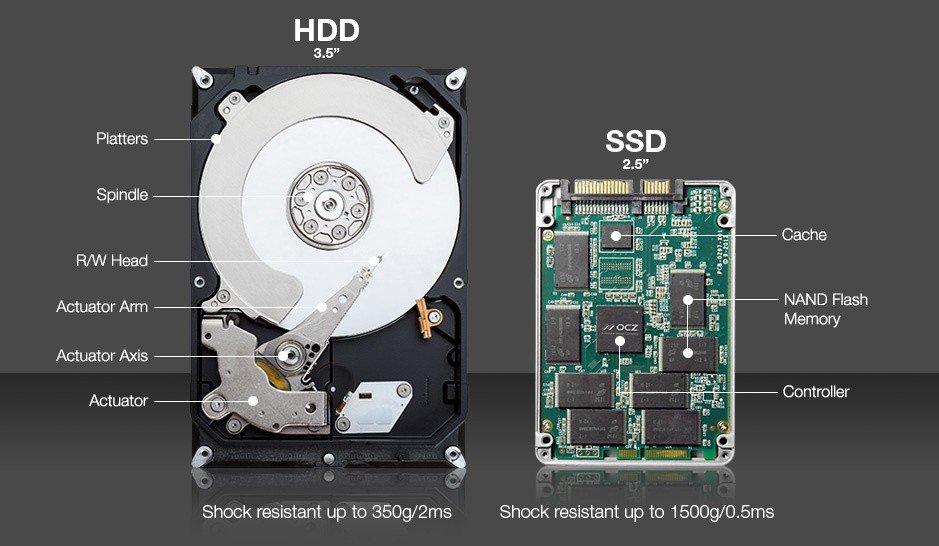
An SSD performs the same basic function as a hard drive, but all information is stored in interconnected flash memory chips that protect data even when there is no power flow. These flash chips (often referred to as “NAND”) are a different type of type used in USB flash drives and are often faster and more reliable. As a result, SSDs are more expensive than USB flash drives of the same capacity.
SSDs are usually much smaller than HDDs, so they provide a lot of flexibility when building systems. We can use them in traditional 2.5-inch or 3.5-inch hard drive bays (SATA). On the other hand, it is possible to install drives known as “M. 2” into a PCI Express expansion slot on the motherboard. This reduces the clutter of the wires.
Benefits of SSDs
Let's talk quickly about the benefits of SSDs.
Durability
Traditional hard drives include moving parts, as we mentioned. These often cause hard disk failures and cause heat generation, another important factor. Because SSDs do not have moving parts, they are more reliable and impact resistant than traditional hard drives. Most hard drives put the read/write heads on hold when the system is off, but they move over a few nanometers over the drive plate while it is running.
As a result, solid state drives are not small, damaged, so we can safely say they are more resistant to drops, accidents, wear and tear. If you drop your laptop and an SSD is installed, your screen will probably break before the SSD. If you are not careful about carrying in general, you should always choose an SSD.
Much faster
This is exactly where the SSDs shine. A PC with an SSD is typically powered on in less than a minute, in just seconds. With HDDs, these times are times higher. On the other hand, your hard drive will still be slower than the SSD in every scenario you use the system.
A PC or Mac with SSD opens faster, starts, runs applications faster, and can transfer files faster. Whether you're using your PC for entertainment, school or business, you'll notice the difference in SSD in any situation.

Magnetic disks have a significant disadvantage. Because of the rolling registration surfaces, hard drives work better with larger files arranged in adjacent blocks. The drive head can start and finish reading with a single continuous movement. When the hard disks start to fill, large pieces of file are scattered around the disk plate and data starts to crumble. Although read/write algorithms minimize this negative impact, by nature, file reading on hard drives is progressing in a slower process. On SSDs, data can be stored anywhere on the drive and is easier to access. Naturally, solid-state drives run much faster.
Portability
SSDs are lighter and smaller than hard drives, making it easier to carry. It also has a sturdy construction that's more durable for falling and crashing, so you can take it with you in comfort.
Because the hard drives are based on rotating plates, there is a certain limit to which the product can shrink. Years ago, there were attempts to develop smaller 1.8-inch hard drives, but they were blocked at 320 GB. Smartphone manufacturers use only flash memory for their primary storage.

SSDs do not have this limitation, so they can continue to shrink as time passes. SATA SSDs are available in 2.5" sizes. On the other hand, products that use the M. 2 connection (NVMe and SATA variants are available) continue to replace SATA-connected SSDs. As you know, these drivers come in lengths of 42 mm, 60 mm, 80 mm and 120 mm.
Efficiency
Solid state drives that run on NAND flash chips do not have moving parts that work, and as a result, they need less power. This means quiet operation and better battery life
None of the energy consumed by the SSD is wasted as friction or noise, making them more efficient. This means that desktop or servers are contributing positively to the electricity bill, regardless of whether it is a desktop or a server. You can work longer on a laptop or tablet.
Easy Set-up
With a screwdriver, we can easily set SSDs. Plus, it's a little more hassle-free to install products that come in the M. 2 form factor.
SSD Form Factors
Solid-state drives are defined by three form factors. These: The size of the drive, the type of connection interface, and the physical space the drive will occupy on the computer.

2.5" SATA SSD
The standard form factor for an SSD is 2.5 inches that fits into the drive bay of most laptops or desktops. Because many users replace their hard drives with solid state drives, the 2.5-inch drive has become a standard for all HDDs and SSDs. Designed to make switching to a higher-performance drive as easy as possible, minimizing the need to replace connection interface cables.
MSATA SSD
MSATA SSDs are small in size compared to SATA. The mSATA can be plugged into the mSATA socket on the motherboard, the size of one-eighth of a 2.5-inch drive. MSATA drives are used as secondary drives in ultra-thin mini devices or desktops.
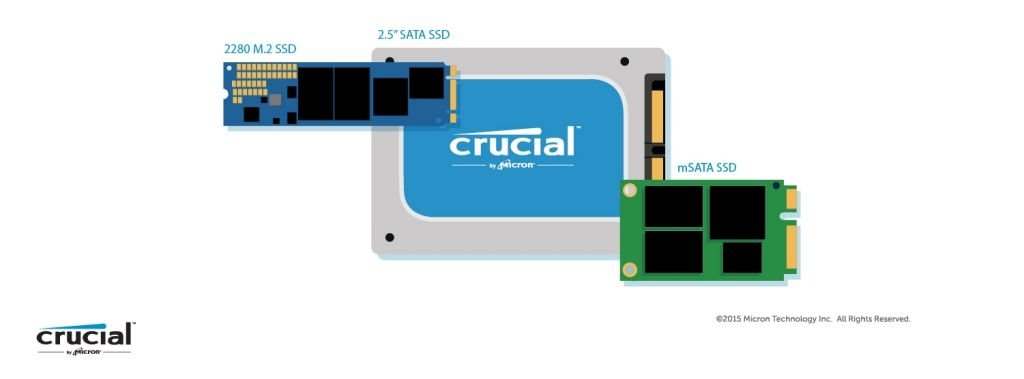
M. 2 SSD
The smallest form factor for SSDs. It is also possible to use in PCIe slots with some adapters when installing on the motherboard via the M. 2 interface. M. 2 SSDs are available in all areas, but they are perfect for small tablets and laptops.
Summary
As a result, SSDs have numerous advantages. Solid state drives deliver faster installation times for games, applications, and movies. However, when used for business purposes, it can significantly shorten the hours and make your work easier.
In fact, there's only one downside: Prices. Although SSD prices continue to be cheaper every day, they are still behind HDDs in terms of price/capacity ratio. But whatever happens, let's end it by saying that at least one SSD should be available on each computer at this time.



Moderatör tarafında düzenlendi:











