^
^
Hello dear members of the Turkish hacking team, I @Arenklord have appreciated quantum computers, which are one of the main pillars of the modern technology world
have a good read..
What is a Quantum Computer?
Quantum computers are machines that use the properties of quantum physics to store data and perform calculations. It is being developed on the basic principles of quantum physics, which tries to explain matter and energy at the atomic and subatomic levels. The electron is processed by controlling the behavior of elementary particles such as protons. Quantum computers, which perform an unimaginable number of operations in the shortest possible time, have much higher processing power and performance than even the best supercomputers in this regard.^
Hello dear members of the Turkish hacking team, I @Arenklord have appreciated quantum computers, which are one of the main pillars of the modern technology world
have a good read..
What is a Quantum Computer?
Quantum computing began in the early 1980s, when physicist Paul Benioff proposed a quantum mechanical model of the Turing machine. Physicist Richard Feynman and mathematician Yuri Manin later proved that it was impossible to simulate quantum systems on a classical computer and became pioneers of the idea of a quantum computer, suggesting that only a quantum computer had the potential to simulate things that a classical computer could not.
How does a Quantum Computer work?
Let's try to explain the working logic by making comparisons over classical computers. Classical computers (smartphone, laptop and desktop computers, etc.) they perform their operations with the help of “Bits” (Binary digit) that can be based on the values of 0 and 1, which we call the binary number system. This system is based on the fact that the electric current on a circuit is switched on and off with the help of a switch. The on state of the switch is expressed as 0, the off state is expressed as 1. A “Byte” is formed by combining eight 1s and 0s Decoupled. It consists of 1 Kilo Byte (KB) with 1024 Bytes, 1 Mega Byte (MB) with 1024 KB. All operations performed on the computer are performed by converting to 0 and 1 at the end.
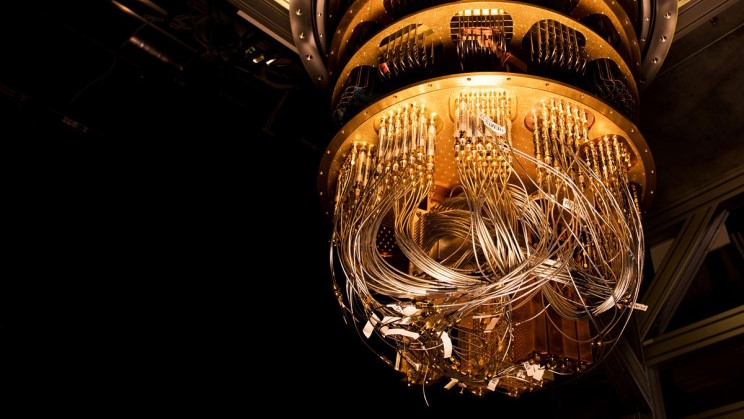

In quantum computing, on the other hand, “Qubit” (Quantum-bit) is used instead of the concept of “Bit” as the basic unit of memory. In a classical computer operating with a binary code system, a bit can only be 1 or 0, while in a quantum computer, a qubit can consist of very different combinations of these 1 and 0 at the same time. This situation is expressed by “superposition”.
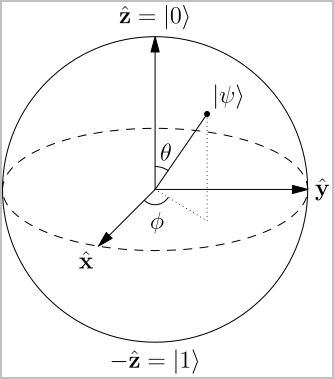

Bloch Sphere - Representation of a qubit (Any point on a three-dimensional sphere shows the state of the qubit.)
Qubits allow a lot of possibilities, since they can simultaneously take both the value 0 and the value 1 (it can happen in both cases at the same time). In other words, 1s and 0s or 0s and 1s can represent information simultaneously. Thanks to these possibilities, quantum machines can calculate all the probabilities in a calculation at once and process much faster than classical computers. In a quantum computer, operations are performed simultaneously instead of being sequenced, unlike classical computers.
In short, quantum computers work not according to the electric current, but with a system based on the physical properties of subatomic particles such as electrons and protons. Thanks to this, they can work at a much greater speed at the subatomic level than classical computers from a much smaller space. Quantum computers have an extremely sensitive structure, so they require special design.
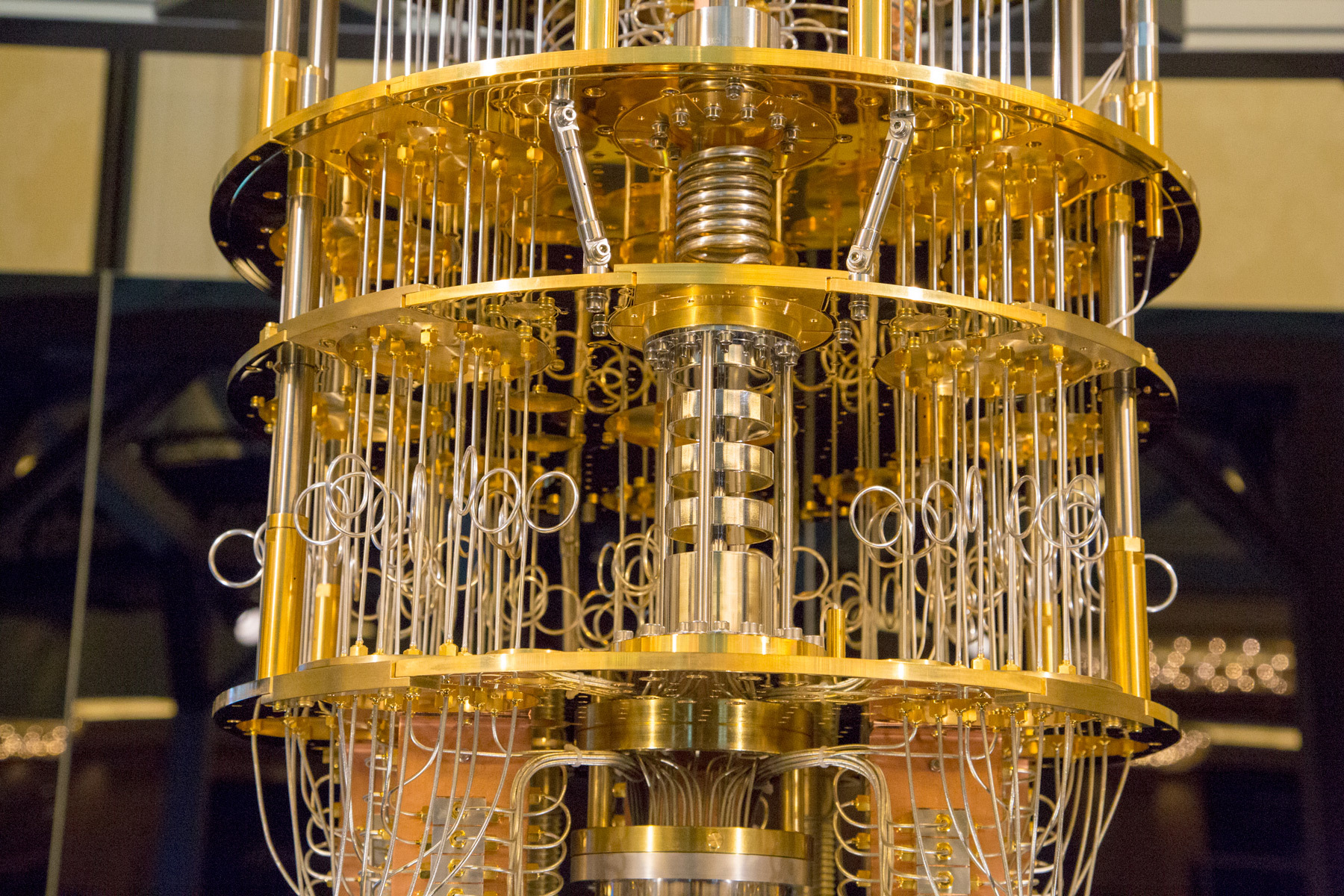
Data Storage in Quantum
The electrons contained in the atom move like magnets due to the magnetic field they have. The property of an electron to behave like a magnet is called “spin” (the angular momentum of a particle in physics). When you put an electron completely isolated from external factors into a magnetic field, they change direction in the direction of the magnetic field under the influence of the magnetic force. That is, they can be found either in the ”spin up“ (upward direction) or in the ”spin down" (downward direction) state. This situation shows us that a single qubit can carry much more information than a standard bit, which means that the “0” and “1” states in a classical computer can have both at the same time, making more possibilities and combinations possible.
Quantum computers are quite sensitive for now: heat, electromagnetic fields, and collisions with air molecules can cause a qubit to lose its quantum properties. This process, known as quantum mismatch, causes the system to collapse, and this process happens faster when more particles are included.
Quantum computers need to protect qubits from outside interference by physically isolating them, keeping them cool, or keeping them away from controlled pulses of energy. In order to eliminate the effects that may come from the external environment, the quantum computer must operate in an environment very close to the absolute temperature of -273 degrees. Such low temperatures can only be achieved by cooling the chip with the help of liquefied helium.
Quantum supremacy
The concept of quantum supremacy, first put forward by California Institute of Technology professor John Preskill in 2012, refers to the condition that problems that are impossible to solve with classical computers or will take a very long time can be solved with quantum computers.
According to an article in the popular science magazine Nature, Google claimed in October 2019 that a 54-qubit quantum computer it called “Sycamore” solved the process that the fastest existing supercomputers could solve in 10 thousand years in 200 seconds, thus announcing that they have quantum supremacy. IBM, on the other hand, stated that there was an error in Google's calculation, and that the problem solved by a quantum computer could be solved by a classical computer in 2.5 days. However, although the enormous difference between 200 seconds and 2.5 days is not as dramatic as Google claims, we can say that it is a major turning point for the technology world Dec.
According to the Xinhua News Agency, the quantum computer called “Jiuzhang” with a 76-qubit processing power, developed by the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) in December 2020, is said to be 10 billion times faster than the Sycamore developed by Google.
As the number of qubits increases, the speed, storage and memory capacity of a quantum computer also increases exponentially. It is stated that a quantum computer that can be used for general purposes will need 1 million qubits.
i hope it will help
@Arenklord , regards...
@Arenklord , regards...












